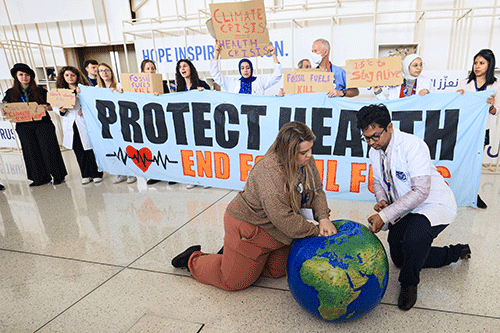
DUBAI – With 2023 confirmed to be the hottest year on record by Europe’s climate monitor, the temperature was also rising Wednesday on negotiators thrashing out the thorny issue of fossil fuels at COP28 in Dubai. Pressure for progress is mounting as the UN climate talks near the end of their first week, with the latest draft of a global climate agreement “probably” expected Wednesday before it is finalised, in theory, on December 12, said one observer.
The fate of oil, gas and coal — the main drivers of human-caused planet heating — has been the biggest sticking point on the agenda, and divisions around their future have dominated the conference. The situation is “very dynamic”, one negotiator said on Tuesday evening, as representatives of nearly 200 countries haggle over the text that responds to a damning stocktake of progress on limiting warming.
Battle lines have previously been drawn on whether to agree to “phase out” or “phase down” fossil fuels. A new phrase committing to an “orderly and just” phase-out of fossil fuels could signal a consensus candidate, giving countries different timelines to cut emissions depending on their level of development and reliance on hydrocarbons.
But there is another option: no mention at all of fossil fuels, which reflects opposition from nations including Saudi Arabia, Russia and China, according to several observers who attended the closed meetings. India on Tuesday evening also opposed naming specific sectors or energy sources, one observer said.
The Paris Agreement that emerged from COP21 in 2015 was a “great success for all of us,” Saudi Arabia’s chief climate negotiator Khalid Almehaid told the Atlantic Council’s Global Energy Forum on Tuesday. “The challenge that we have today is how can we keep that train with all of its passengers,” he added, alluding to the kingdom’s objection to phasing down fossil fuels.
But some of the countries that are most vulnerable to climate change on Wednesday urged called for a harder stance on fossil fuels. The Alliance of Small Islands States “calls on major emitters to enhance their commitments, including… leading the way on fossil fuel phase out, phasing out all fossil fuel subsidies, and ensuring peaking of global emissions before 2025 and halving them by 2030,” the group’s chair Cedric Schuster said in a statement.
As it stands, the draft agreement includes options to phase out fossil fuels or not address the issue at all, setting the stage for tough negotiations due to end next week. Climate experts, however, have warned that global warming could breach the 1.5 degrees Celsius Paris deal limit within seven years if emissions are not slashed.
The new draft of the negotiated text expected on yesterday must be brought to a large plenary meeting taking stock of the first week of talks ahead of a rest day today. – Nampa/AFP